What is MolSurfer?
Description
Molsurfer is based on JSMol and replaces the former java based software. It uses the representation of the macromolecular interface generated by adsi (the interface module of ads, analytically defined molecular surfaces ) and JSmol, a JavaScript implementation of Jmol. (Java plugins have recently become very restrictive, due to many security concerns.)
It can be used to study protein-protein and protein-DNA/RNA interfaces. The 2D projections of the computed interface aid visualization of complicated interfacial geometries in 3D. Molecular properties, including hydrophobicity and electrostatic potential, can be projected onto the interface. MolSurfer can thereby aid exploration of molecular complementarity, identification of binding "hot spots" and prediction of the effects of mutations. MolSurfer can also facilitate the location of cavities at macromolecular interfaces.
Links to MolSurfer
You can generate links to molsurfer, allowing the analysis of interfaces in RCSB entries. For this the URL parameters pdbidinput, chainid1 and chainid2 needs to be specified in the following manner:
http://molsurfer.h-its.org/cgi-bin/molsurfer_master.cgi?pdbidinput=1hbb&chainid1=A&chainid2=B,C,D
Just replace the bold parts of the URL above with the information about your PDB entry.
Problems with PDB files
In some cases molsurfer will not work on some uploaded PDB files. If the files have missing columns or coordinates with large numbers. In these cases you can use this script to move the protein to the center of the coordinate system, resulting in smaller numbers for the coordinates. The script can be called with the pdb file to process as argument. It will write a file with '-moved-origin' appended. Use this to upload to molsurfer. The script requires python3, biopython and numpy installed. It was tested on linux only.
Details of Interface Mapping and Displayed Properties
- A quasi rectangular mesh with 1 Å spacing was generated on the analytically defined interface between these 2 macromolecules.
- Points for which the sum of the distances to the closest atoms of macromolecule I and II exceeds 6 Å were deleted.
- Heteroatoms that lie within 3 Å of any interface point were added.
- The properties of each macromolecule were projected onto every point of the interface; these are the properties assigned to the closest atom to the point.
- Residue hydrophobicities were assigned according to the residue name and following the parameters in Eisenberg D., Weiss R.M., Terwilliger T.C. and Wilcox W. (1982) Farad. Symp. Chem. Soc., 17, 109-120, namely:
- Atomic hydrophobicities were assigned according to the atom name and follow Eisenberg D., Wesson M., Yamashita M. (1989) Chem. Scrip., 29A, 217-221, namely:
- Atomic radii were also assigned from the previous reference, namely:
- Electrostatic potential of each (isolated) macromolecule was computed with the APBS program and the potential values were interpolated at each interface point.
- Additional plots are shown for the similarities of electrostatic potential, atomic and residue similarities as well as B-Factor similarity.
The similarities are calculated according to Hodgkin and Richards (Journal of Quantum Chemistry, 1987). Regions where both sides of the interface are very similar have values of approx. 1. Anticorrelated areas have values of -1. Uncorrelated areas near 0.
- Additionally, the changes in binding free energy upon alanine mutation were assigned to each side-chain atom of the corresponding residue. This data can be obtained from the Alanine Scanning Energetics database for example.
ALA 0.25 GLN -0.69 LEU 0.53 SER -0.26
ARG -1.80 GLU -0.62 LYS -1.10 THR -0.18
ASN -0.64 GLY 0.16 MET 0.26 TRP 0.37
ASP -0.72 HIS -0.40 PHE 0.61 TYP 0.02
CYS 0.04 ILE 0.73 PRO -0.07 VAL 0.54
none of the above 0.00
'NZ LYS' -38 'OE1 GLU' -37 'C' 18
'NH1 ARG' -38 'OE2 GLU' -37 'S' 5
'NH2 ARG' -38 'OD1 ASP' -37 'O' -9
'OD2 ASP' -37 'N' -9
none of the above 0
'C' 1.9 A
'S' 1.8 A
'O' 1.4 A
'N' 1.7 A
none of the above 1.9 A
More details can be found in Analytically Defined (molecular) Surfaces website. The standalone version of MolSurfer can be downloaded from the previous MolSurfer website.
References
- R.R. Gabdoulline, R.C. Wade & D. Walther (2003) MolSurfer: a macromolecular interface navigator, Nucleic Acids Research, 31, 3349-3351. abstract and full text
- R.R. Gabdoulline, R.C. Wade & D. Walther. (1999) MolSurfer: two dimensional maps for navigating three-dimensional structures of proteins, Trends Biochem. Sci., 24, 285-287 . (excerpt)
Application Examples
MolSurfer applications citing the first reference above.
other examples:- Hough MA, Hall JF, Kanbi LD, Hasnain SS. (2001) Structure of the M148Q mutant of rusticyanin at 1.5 angstrom: a model for the copper site of stellacyanin, Acta Crystallogr D, 57, 355-360.
- Luedemann SK, Gabdoulline RR, Lounnas V, Wade RC, Substrate access to cytochrome P450cam investigated by molecular dynamics simulations: An interactive look at the underlying mechanisms, Internet. J. Chem. (2001) 4, 6. (abstract)
- Campbell JD, Biggin PC, Baaden M, Sansom MSP (2003) Extending the structure of an ABC transporter to atomic resolution: Modeling and simulation studies of MsbA, Biochemistry, 42 (13), 3666-3673.
- Flaus A, Rencurel C, Ferreira H, Wiechens N, Owen-Hughes T (2004) Sin mutations alter inherent nucleosome mobility, EMBO Journal, 23, 343-353.
- Wang T, Tomic S, Gabdoulline RR, Wade RC (2004) How optimal are the binding energetics of barnase and barstar? Biophys J. 87, 1618-30.
- Huelsmeyer M, Chames P, Hillig RC, Stanfield RL, Held G, Coulie PG, Alings C, Wille G, Saenger W, Uchanska-Ziegler B, Hoogenboom HR, Ziegler A, (2005) A Major Histocompatibility Complex Peptide-restricted Antibody and T Cell Receptor Molecules Recognize Their Target by Distinct Binding Modes (A Major Histocompatibility Complex Peptide-restricted Antibody and T Cell Receptor Molecules Recognize Their Target by Distinct Binding Modes), J. Biol. Chem. 280, 2972-2980.
- K�vesi I, Schay G, Yonetani T, Laberge M, Fidy J, (2005) High pressure reveals that the stability of interdimeric contacts in the R- and T-state of HbA is influenced by allosteric effectors: Insights from computational simulations, Biochim Biophys Acta, 1764, 516-21.
MolSurfer Example Usage
MolSurfer Usage
MolSurfer can used in three different ways. This mainly differs by the starting parameters used to launch MolSurfer:
- Molsurfer analysis using PDB identifier as input
- Molsurfer analysis using PDB file(s) as input
- Molsurfer analysis including electrostatic properties
- Display the analysis result.
Molsurfer analysis using PDB identifier as input
The default input form for Molsurfer allows the input of a PDB identifier together with two sets of chain ID's as can be seen on the following screenshot.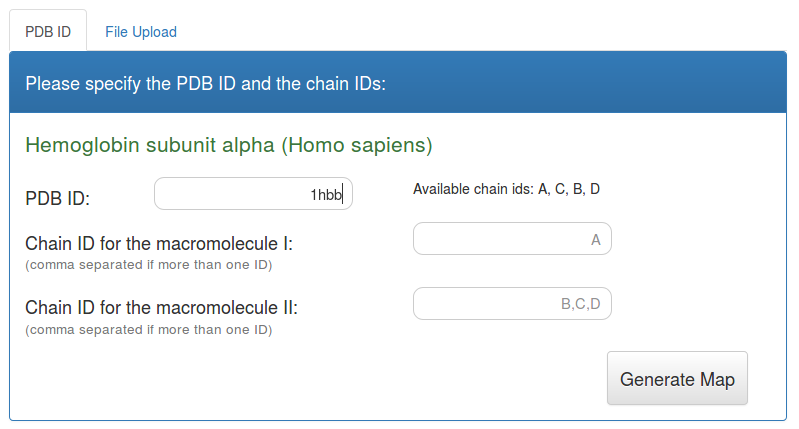
As soon as you enter a valid PDB ID, the search panel shows the title of the respective entry as well as the available chain IDs for this entry.
You need to select two groups of macromolecules in the entry fields for the chain id. Molsurfer will then calculate the properties of the interface between these two groups of molecules.
Starting with PDB IDs does not allow to calculate electrostatic potentials. For this you will need to calculate the corresponding PQR files for the group of macromolecules yourself and use the input that allows the upload of PQR files, see below.
Molsurfer Analysis using PDB file(s) as input
You can also analyse your own PDB files. For this, the chains that form the interface you are interested can be in a single file or in two files. The input for allows you to select between the upload of one or two files. In case you select one file, you also need to give the group of chain IDs, that form the interface, just like in the input form for the PDB ID above.
As example, you can download the following two PDB files: 1AIQ_A.pdb
and 1AIQ_B.pdb and select them in the input form.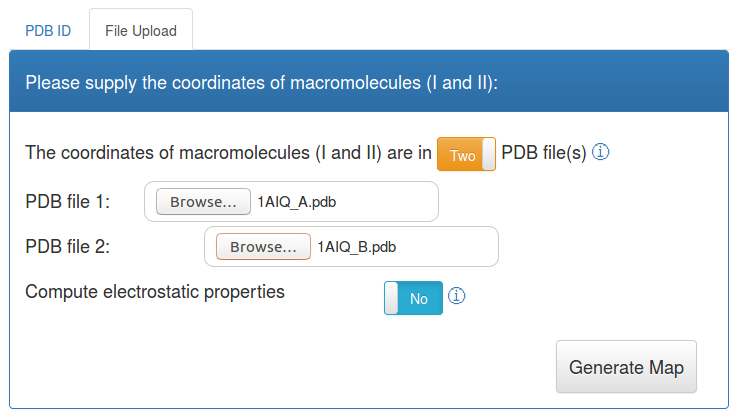
Pressing the button: Generate Map will execute the analysis. If you also want to compute electrostatic properties, please continue here.
Molsurfer Analysis including electrostatic properties
]To also calculate electrostatic potentials on the interface, you need to also upload PQR files, that correspond to the group of macromolecules that form the interface you are interested in. You can use the PDB2PQR server to calculate these files.
Since the electrostatic potential is different for the molecules on the two sides of the interface, you need to calculate two PQR files, that correspond to your selection of macromolecules that form the interface of interest.
As an example, extending the example above, you can download the 1AIQ_A.pqr and 1AIQ_B.pqr file and use it for an example calculation. The corresponding input form is shown below.
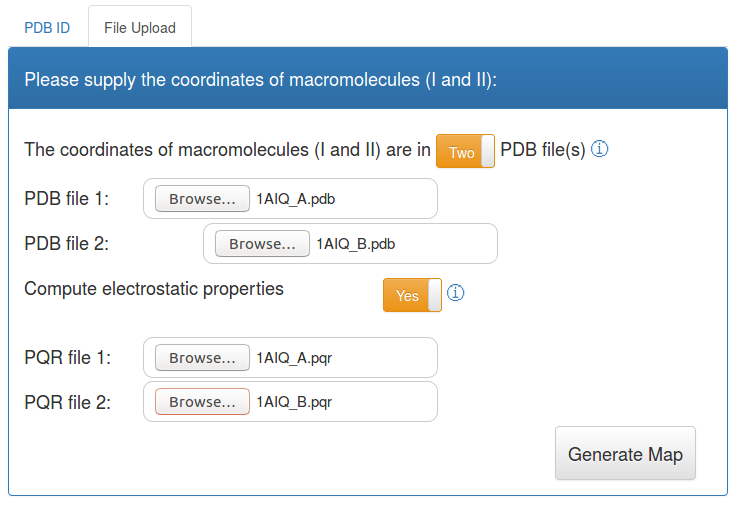
Display the analysis result
All three input methods will be started by pressing the "Generate Map" button. The result shows on the left 2D maps of the interface with selected properties like On the right you get a 3D view of the interface in a JSMol display. The currently selected property is color mapped to the displayed interface in the 3D structure display. You can modify the 3D display via the menu on the website, or via the context menu of the JSMol display (right click on the structure display). An example display is shown below.
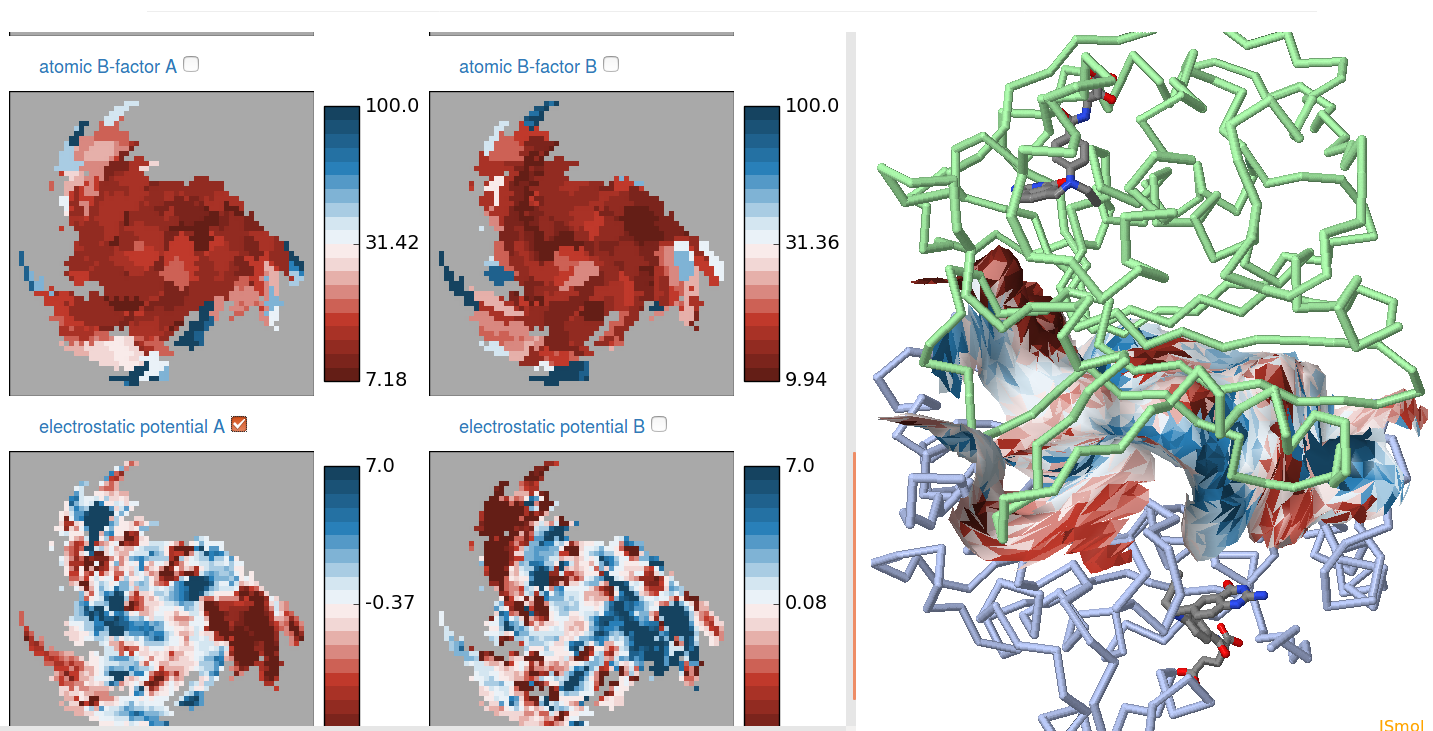
You can explore the interace using the mouse. Corresponding positions on
all 2D maps will be shown as well as on the 3D structure view.
MolSurfer Demonstration Cases
The original MolSurfer distribution from 1999 included demonstration cases for 35 protein-protein interfaces as well as 75 protein-DNA/RNA interfaces. These original calculations are offered here as demonstration cases.
They include calculated electrostatic properties.
| Code | Molecule 1 | Molecule 2 | ProSat+ link |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1acb | ALPHA-CHYMOTRYPSIN | Eglin C | ProSAT+ |
| 1atn | ACTIN | DEOXYRIBONUCLEASE I | ProSAT+ |
| 1bql | HYHEL-5 FAB (HEAVY CHAIN) | BOBWHITE QUAIL LYSOZYME | ProSAT+ |
| 1brs | BARNASE | BARSTAR | ProSAT+ |
| 1cho | ALPHA-CHYMOTRYPSIN A | TURKEY OVOMUCOID THIRD DOMAIN (OMTKY3) | ProSAT+ |
| 1cse | SUBTILISIN CARLSBERG | EGLIN C | ProSAT+ |
| 1dvf | FV D1.3 | FV E5.2 | ProSAT+ |
| 1fbi | IGG1 F9.13.7 FAB (HEAVY CHAIN) | GUINEA FOWL LYSOZYME | ProSAT+ |
| 1fc2 | IMMUNOGLOBULIN FC | FRAGMENT B OF PROTEIN A COMPLEX | ProSAT+ |
| 1fdl | IGG1-KAPPA D1.3 FAB (HEAVY CHAIN) | HEN EGG WHITE LYSOZYME | ProSAT+ |
| 1gla | GLYCEROL KINASE | GLUCOSE-SPECIFIC PROTEIN IIIGlc | ProSAT+ |
| 1hwg | GROWTH HORMONE | GROWTH HORMONE BINDING PROTEIN | ProSAT+ |
| 1jhl | IGG1-KAPPA D11.15 FV (HEAVY CHAIN) | PHEASANT EGG WHITE LYSOZYME | ProSAT+ |
| 1jrh | ANTIBODY A6 | INTERFERON-GAMMA RECEPTOR ALPHA CHAIN | ProSAT+ |
| 1lpa | LIPASE | COLIPASE | ProSAT+ |
| 1mah | ACETYLCHOLINESTERASE | FASCICULIN 2 | ProSAT+ |
| 1mlc | IGG1-KAPPA D44.1 FAB (HEAVY CHAIN) | HEN EGG WHITE LYSOZYME | ProSAT+ |
| 1nca | INFLUENZA A SUBTYPE N9 NEURAMINIDASE | IGG2A-KAPPA NC41 FAB (HEAVY CHAIN) | ProSAT+ |
| 1ppf | HUMAN LEUKOCYTE ELASTASE | TURKEY OVOMUCOID INHIBITOR (OMTKY3) | ProSAT+ |
| 1tab | TRYPSIN | BOWMAN-BIRK TYPE PROTEINASE INHIBITOR | ProSAT+ |
| 1tec | THERMITASE | EGLIN C | ProSAT+ |
| 1tgs | TRYPSINOGEN | PANCREATIC SECRETORY TRYPSIN INHIBITOR (KAZAL TYPE) | ProSAT+ |
| 1tpa | ANHYDRO-TRYPSIN | BOVINE PANCREATIC TRYPSIN INHIBITOR | ProSAT+ |
| 1vfb | IGG1-KAPPA D1.3 FV (HEAVY CHAIN) | HEN EGG WHITE LYSOZYME | ProSAT+ |
| 1yqv | HyHEL-5 Antibody Heavy Chain | Hen Egg White Lysozyme | ProSAT+ |
| 2kai | KALLIKREIN A | BOVINE PANCREATIC TRYPSIN INHIBITOR | ProSAT+ |
| 2pcb | CYTOCHROME C PEROXIDASE (CCP) | CYTOCHROME C | ProSAT+ |
| 2ptc | BETA-TRYPSIN | TRYPSIN INHIBITOR | ProSAT+ |
| 2sec | SUBTILISIN CARLSBERG | EGLIN C | ProSAT+ |
| 2sic | SUBTILISIN BPN' | STREPTOMYCES SUBTILISIN INHIBITOR (SSI) | ProSAT+ |
| 2sni | SUBTILISIN NOVO | CHYMOTRYPSIN INHIBITOR 2 | ProSAT+ |
| 2tgp | TRYPSINOGEN | TRYPSIN INHIBITOR | ProSAT+ |
| 2tpi | TRYPSIN INHIBITOR | ProSAT+ | |
| 3hfm | HYHEL-10 IGG1 FAB (HEAVY CHAIN) | HEN EGG WHITE LYSOZYME | ProSAT+ |
| 3hhr | HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE | HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE RECEPTOR (hGHbp) | ProSAT+ |
| 3sgb | PROTEINASE B (SGPB) | TURKEY OVOMUCOID INHIBITOR (OMTKY3) | ProSAT+ |
| 4cpa | METALLOCARBOXYPEPTIDASE INHIBITOR | ProSAT+ | |
| 4ins | INSULIN (CHAIN B) | INSULIN (CHAIN B) | ProSAT+ |
| 4sgb | SERINE PROTEINASE B | POTATO INHIBITOR, PCI-1 | ProSAT+ |
| 4tpi | BOVINE PANCREATIC TRYPSIN INHIBITOR | ProSAT+ | |
| 6rlx | RELAXIN, B-CHAIN | RELAXIN, B-CHAIN | ProSAT+ |
| 1a3q | PROTEIN (NUCLEAR FACTOR KAPPA-B P52) | DNA (5'-D(*GP*GP*GP*GP*AP*TP*TP*CP*CP*CP*C)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1aay | PROTEIN (ZIF268 ZINC FINGER PEPTIDE) | DNA (5'-D(*TP*AP*CP*GP*CP*CP*CP*AP*CP*GP*C)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1ais | PROTEIN (TRANSCRIPTION INITIATION FACTOR IIB) | DNA (5'-D(*GP*CP*TP*TP*TP*AP*AP*AP*AP*AP*GP*TP*AP*AP*GP*TP*T )-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1an2 | ProSAT+ | ||
| 1an4 | PROTEIN (UPSTREAM STIMULATORY FACTOR) | DNA (5'-D(*GP*TP*GP*TP*AP*GP*GP*CP*CP*AP*CP*GP*TP*GP*AP*CP*C P*GP*GP*GP*T)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1apl | PROTEIN (MAT-ALPHA2 HOMEODOMAIN) | DNA (5'-D(*TP*GP*CP*GP*TP*GP*TP*AP*AP*AP*TP*GP*AP*AP*TP*TP*A P*CP*AP*TP*G)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1asy | ASPARTYL-tRNA SYNTHETASE | T-RNA (75-MER) | ProSAT+ |
| 1bhm | PROTEIN (BAMHI (E.C.3.1.21.4)) | DNA (5'-D(*TP*AP*TP*GP*GP*AP*TP*CP*CP*AP*TP*A)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1bpy | PROTEIN (DNA POLYMERASE BETA) | DNA (5'-D(*GP*TP*CP*GP*G)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1brn | PROTEIN (BARNASE (E.C.3.1.27.-)) | DNA (5'-D(*CP*GP*AP*C)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1cdw | PROTEIN (TATA BINDING PROTEIN (TBP)) | DNA (5'-D(*CP*AP*GP*CP*CP*TP*TP*TP*TP*AP*TP*AP*GP*CP*AP*G)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1cma | PROTEIN (MET REPRESSOR) | DNA (5'-D(*AP*GP*AP*CP*GP*TP*CP*TP*A)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1d66 | PROTEIN (GAL4) | DNA (5'-D(*CP*CP*GP*GP*AP*GP*GP*AP*CP*TP*GP*TP*CP*CP*TP*CP*C P*GP*G)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1dct | PROTEIN (MODIFICATION METHYLASE HAEIII) | DNA (5'-D(*TP*CP*AP*CP*TP*GP*GP*TP*GP*GP*(C5M)P*CP*TP*GP*CP*TP*GP*G)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1dnk | PROTEIN (DEOXYRIBONUCLEASE I (DNASE I) (E.C.3.1.21.1)) | DNA (5'-D(*GP*GP*TP*AP*TP*AP*CP*C)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1ecr | PROTEIN (REPLICATION-TERMINATOR PROTEIN) | DNA (5'-D(*TP*AP*GP*TP*AP*TP*GP*TP*TP*GP*TP*AP*AP*CP*TP*A)-3 | ProSAT+ |
| 1eri | PROTEIN (ECO RI ENDONUCLEASE (E.C.3.1.21.4)) | DNA (5'-D(*TP*CP*GP*CP*GP*AP*AP*TP*TP*CP*GP*CP*G)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1fjl | PAIRED PROTEIN | DNA (5'-D(*TP*GP*TP*AP*AP*TP*CP*AP*GP*AP*TP*TP*AP*T)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1fok | PROTEIN (FOKI RESTRICTION ENDONUCLEASE) | DNA (5'-D(*AP*TP*GP*AP*CP*TP*AP*GP*CP*GP*TP*TP*AP*TP*CP*AP*T P*CP*CP*G)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1fos | C-JUN PROTO-ONCOGENE PROTEIN | DNA (5'-D(*TP*TP*CP*TP*CP*CP*TP*AP*TP*GP*AP*CP*TP*CP*AP*TP*CP*CP*AP*T)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1gdt | PROTEIN (GAMMA DELTA RESOLVASE) | SITE I OF RES DNA | ProSAT+ |
| 1glu | PROTEIN (GLUCOCORTICOID RECEPTOR) | DNA (5'-D(*CP*CP*AP*GP*AP*AP*CP*AP*TP*CP*GP*AP*TP*GP*TP*TP*C P*TP*G)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1gtr | GLUTAMINYL-tRNA SYNTHETASE | RNA (74-MER) | ProSAT+ |
| 1hcq | PROTEIN (ESTROGEN RECEPTOR) | DNA (5'-D(*CP*CP*AP*GP*GP*TP*CP*AP*CP*TP*GP*TP*GP*AP*CP*CP*T P*G)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1hcr | PROTEIN (HIN RECOMBINASE) | DNA (5'-D(*TP*CP*TP*TP*AP*TP*CP*AP*AP*AP*AP*AP*C)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1hdd | PROTEIN (ENGRAILED HOMEODOMAIN) | DNA (5'-D(*AP*TP*TP*AP*GP*GP*TP*AP*AP*TP*TP*AP*CP*AP*TP*GP*G P*CP*AP*AP*A)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1hlo | PROTEIN (TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR MAX) | DNA (5'-D(*AP*CP*CP*AP*CP*GP*TP*GP*GP*TP*G)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1hut | ALPHA-Thrombin heavy chain | DNA 5'-D(*GP*GP*TP*TP*GP*GP*TP*GP*TP*GP*GP*TP*TP*GP*G)-3' | ProSAT+ |
| 1ign | PROTEIN (RAP1) | DNA (5'-D(*CP*CP*TP*GP*GP*TP*GP*TP*GP*TP*GP*GP*GP*TP*GP*TP*G P*CP*G)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1ihf | PROTEIN (INTEGRATION HOST FACTOR (BETA) (IHF)) | ProSAT+ | |
| 1jmc | PROTEIN (REPLICATION PROTEIN A (RPA)) | DNA (5'-D(*CP*CP*CP*CP*CP*CP*CP*C)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1kln | PROTEIN (DNA POLYMERASE I KLENOW FRAGMENT (E.C.2.7.7.7)) | DNA (5'-D(*GP*CP*CP*TP*CP*GP*CP*GP*GP*CP*GP*GP*C)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1lat | GLUCOCORTICOID RECEPTOR | DNA (5'-D(*TP*TP*CP*CP*AP*GP*AP*AP*CP*AP*TP*GP*TP*TP*CP*TP*G P*GP*A)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1lmb | PROTEIN (LAMBDA REPRESSOR) | DNA (5'-D(*TP*AP*TP*AP*TP*CP*AP*CP*CP*GP*CP*CP*AP*GP*TP*GP*G P*TP*AP*T)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1mdy | PROTEIN (MYOD BHLH DOMAIN) | DNA (5'-D(*TP*CP*AP*AP*CP*AP*GP*CP*TP*GP*TP*TP*GP*A)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1mey | CONSENSUS ZINC FINGER | DNA (5'-D(*TP*AP*GP*TP*TP*CP*TP*GP*CP*CP*TP*(C38)P*A)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1mht | PROTEIN (HHAI METHYLTRANSFERASE) | DNA (5'-D(*TP*GP*AP*TP*AP*GP*(C36)P*GP*CP*TP*AP*TP*C)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1nfk | PROTEIN (NUCLEAR FACTOR KAPPA-B (NF-KB)) | DNA (5'-D(*TP*GP*GP*GP*AP*AP*TP*TP*CP*CP*C)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1oct | PROTEIN (OCT-1 POU DOMAIN) | DNA (5'-D(*AP*CP*CP*TP*TP*AP*TP*TP*TP*GP*CP*AP*TP*AP*C)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1par | PROTEIN (ARC REPRESSOR) | DNA (5'-D(*AP*AP*TP*GP*AP*TP*AP*GP*AP*AP*GP*CP*AP*CP*TP*CP*T P*AP*CP*TP*AP*T)- 3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1pdn | PROTEIN (PRD PAIRED) | DNA (5'-D(*TP*TP*GP*TP*CP*AP*AP*CP*CP*GP*TP*GP*AP*CP*G)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1per | PROTEIN (434 REPRESSOR) | DNA (5'-D(*TP*AP*TP*AP*CP*AP*AP*GP*AP*AP*AP*AP*AP*CP*TP*GP*T P*AP*CP*T)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1pue | PROTEIN (TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR PU.1 (TF PU.1)) | DNA (5'-D(*TP*CP*CP*CP*AP*CP*TP*TP*CP*CP*CP*CP*TP*TP*TP*T)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1pvi | PROTEIN (PVUII (E.C.3.1.21.4)) | DNA (5'-D(*TP*GP*AP*CP*CP*AP*GP*CP*TP*GP*GP*TP*C)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1pyi | PROTEIN (PYRIMIDINE PATHWAY REGULATOR 1) | DNA (5'-D(*TP*CP*GP*GP*CP*AP*AP*TP*TP*GP*CP*CP*GP*A)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1ruo | PROTEIN (CATABOLITE GENE ACTIVATOR PROTEIN (CAP)) | DNA (5'-D(*CP*TP*AP*GP*AP*TP*CP*AP*CP*AP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*CP*G )-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1rvc | PROTEIN (ECO RV (E.C.3.1.21.4)) | DNA (5'-D(*AP*TP*CP*TP*T)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1ser | PROTEIN (SERYL-TRNA SYNTHETASE (E.C.6.1.1.11)) | TRNASER | ProSAT+ |
| 1srs | PROTEIN (SERUM RESPONSE FACTOR (SRF)) | DNA (5'-D(*CP*CP*AP*TP*GP*GP*CP*CP*TP*AP*AP*TP*TP*AP*GP*GP*A P*AP*G)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1svc | PROTEIN (NUCLEAR FACTOR KAPPA-B (NF-KB)) | ProSAT+ | |
| 1t7p | PROTEIN (THIOREDOXIN) | DNA (5'-D(P*CP*CP*TP*TP*GP*GP*CP*AP*CP*TP*GP*GP*C)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1tau | PROTEIN (TAQ POLYMERASE) | DNA (5'-D(*CP*GP*GP*AP*TP*CP*GP*C)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1tc3 | PROTEIN (TC3 TRANSPOSASE) | DNA (5'-D(*AP*GP*TP*TP*CP*TP*AP*TP*AP*GP*GP*AP*CP*CP*CP*CP*C P*CP*CP*T)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1tro | PROTEIN (TRP REPRESSOR) | DNA (5'-D(*TP*GP*TP*AP*CP*TP*AP*GP*TP*TP*AP*AP*CP*TP*AP*GP*T P*AP*C)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1trr | PROTEIN (TRP REPRESSOR) | DNA (5'-D(*AP*GP*CP*GP*TP*AP*CP*TP*AP*GP*TP*AP*CP*GP*CP*T)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1tsr | PROTEIN (P53 TUMOR SUPPRESSOR) | DNA (5'-D(*AP*TP*AP*AP*TP*TP*GP*GP*GP*CP*AP*AP*GP*TP*CP*TP*A P*GP*GP*AP*A)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1ttt | OF ELONGATION FACTOR TU (EF-TU) | TRANSFER RIBONUCLEIC ACID (YEAST, PHE) | ProSAT+ |
| 1uaa | PROTEIN (ATP-DEPENDENT DNA HELICASE REP.) | DNA (5'-D(*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*T)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1ubd | PROTEIN (YY1 ZINC FINGER DOMAIN) | DNA (5'-D(*CP*GP*CP*TP*TP*CP*AP*AP*AP*AP*TP*GP*GP*AP*GP*AP*C P*CP*CP*T)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1urn | PROTEIN (U1A) | RNA (5'-R(*AP*AP*UP*CP*CP*AP*UP*UP*GP*CP*AP*CP*UP*CP*CP*GP*G P*AP*UP*UP*U)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1vas | PROTEIN (T4 ENDONUCLEASE V (E.C.3.1.25.1)) | DNA (5'-D(*TP*AP*GP*CP*GP*CP*AP*AP*CP*GP*CP*GP*A)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1vol | PROTEIN (TATA BINDING PROTEIN (TBP)) | DNA (5'-D(*CP*AP*GP*CP*CP*CP*TP*TP*TP*TP*AP*TP*AP*GP*CP*C)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1wet | PROTEIN (PURINE REPRESSOR) | DNA (5'-D(*AP*AP*CP*GP*AP*AP*AP*AP*CP*GP*TP*TP*TP*TP*CP*GP*T )-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1xbr | PROTEIN (T PROTEIN) | DNA (5'-D(*AP*AP*TP*TP*TP*CP*AP*CP*AP*CP*CP*TP*AP*GP*GP*TP*G P*TP*GP*AP*AP*AP* TP*T)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1yrn | PROTEIN (MAT ALPHA2 HOMEODOMAIN) | DNA (5'-D(*TP*AP*CP*AP*TP*GP*TP*AP*AP*TP*TP*TP*AP*TP*TP*AP*C P*AP*TP*CP*A)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1ysa | PROTEIN (GCN4) | DNA (5'-D(*AP*AP*AP*CP*TP*GP*GP*AP*TP*GP*AP*GP*TP*CP*AP*TP*A P*GP*GP*A)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1ytf | PROTEIN (TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR IIA - TOA2 SUBUNIT) | DNA (5'-D(*GP*TP*TP*TP*TP*AP*TP*AP*TP*AP*CP*AP*TP*AP*CP*A)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1zdi | PROTEIN (RNA BACTERIOPHAGE MS2 COAT PROTEIN) | RNA (5'-R(*AP*CP*AP*UP*GP*AP*GP*GP*AP*UP*UP*AP*CP*CP*CP*AP*U P*GP*U)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 1zme | PROLINE UTILIZATION TRANSCRIPTION ACTIVATOR | DNA (5'-D(*AP*CP*GP*GP*AP*GP*(5IU)P*TP*GP*GP*CP*TP*(5IU)P*CP*CP*CP*G)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 2bop | PROTEIN (E2) | DNA (5'-D(*CP*CP*GP*AP*CP*CP*GP*AP*CP*GP*TP*CP*GP*GP*TP*CP*G )-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 2dgc | PROTEIN (GCN4) | DNA (5'-D(*TP*GP*GP*AP*GP*AP*TP*GP*AP*CP*GP*TP*CP*AP*TP*CP*T P*CP*C)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 2drp | PROTEIN (TRAMTRACK DNA-BINDING DOMAIN) | DNA (5'-D(*TP*CP*GP*GP*AP*CP*GP*TP*TP*AP*TP*CP*CP*TP*TP*AP*T P*TP*A)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 2gli | PROTEIN (FIVE-FINGER GLI) | DNA (5'-D(*AP*CP*GP*TP*GP*GP*AP*CP*CP*AP*CP*CP*CP*AP*AP*GP*AP*CP*GP*AP*A)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 2nll | PROTEIN (THYROID HORMONE RECEPTOR) | DNA (5'-D(*CP*TP*GP*AP*CP*CP*TP*GP*AP*AP*AP*TP*GP*AP*CP*CP*T P*G)-3') | ProSAT+ |
| 3cro | PROTEIN (434 CRO) | DNA (5'-D(*TP*AP*TP*AP*CP*AP*AP*GP*AP*AP*AP*GP*TP*TP*TP*GP*T P*AP*CP*T)-3') | ProSAT+ |
Changes / Known Issues
Authors
- The list of authors of the original version is given here
- A complete reimplementation in python, JSMol and HTML-Bootstrap was performed from Jui-Hung Yuan in 2018.
- The functionality to calculate electrostatic properties on downloaded PDB entries, an overhaul of the demonstration cases and other features was added by Dorothee Groß in 2022.
- General maintainance is done by Stefan Richter (mcmsoft(at)h-its.org)
Issues
- Uploading PDB files not conforming to the standards might cause problems. See the section "Problems with PDB files" on the main documentation page on how to resolve this.
- In case you use an ad blocker with your browser, the JSMol visualization of the protein might not be loaded (Error message "Network error"). In this case, disable your ad blocker or put the molsurfer on the exception list.
- Uploading two files, both without chain id causes an error
- Using two unrelated proteins causes an error
Changes
- Aug/2023 added a downloadable script to fix problems in PDB files with large numbers in coordinate files. See the section "Problems with PDB files" on the main documentation page on how to resolve this.
- July/2022 changed forcefield to AMBER and PDB2PQR to version 3.5.2 to allow also processing of nucleotides. Removed all HET Atoms in the pdb files before pdb2pqr processing. Use ionic strength of the original version (0.15 M instead of 0.05 M, also protein permittivity from 2 to 4 as in the original publication). Display all models in case of NMR structures (only the first one will be used for the calculation)
- 2022 added support for generating electrostatic properties when only PDB ids are submitted (Runs PDB2PQR in the background). Links to log files and data files provided.
- 2021 added similarity maps for hydrophobic and electrostatic properties. This is a reintroduction of a feature from the original implementation
- 2018 reimplementation with JSMol. No Java required any longer.
- Adding the following features:
- Also added the feature to display B-Factor and electrostatic potential information in one run.
- Support to start using PDB identifier
- Dynamically load description and chain information for PDB entries. Chain information for files
- Initial release using Java applet and webmol.